Mutualism promotes site selection in a large marine planktivore
March 2021
Asia O. Armstrong, Amelia J. Armstrong, Michael B. Bennett, Anthony J. Richardson, Kathy A. Townsend, Jason D. Everett, Graeme C. Hays, Hugh Pederson & Christine L. Dudgeon
Keywords: Acoustic Tracking • Animal Navigation • Coral Reef • Elasmobranch • Location Accuracy • Megafauna • Movement Ecology • VEMCO Positioning System
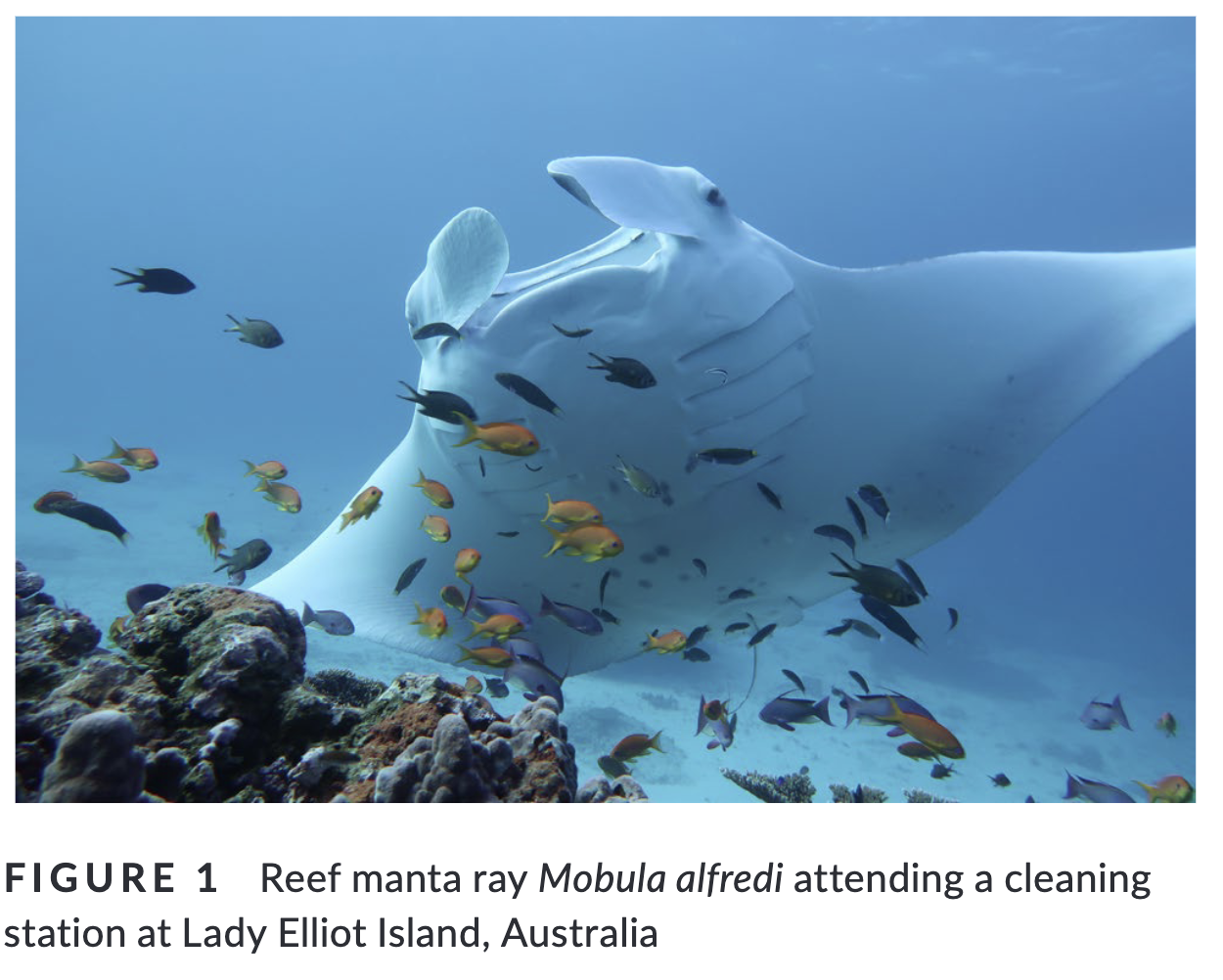

Summary: Cleaning symbiosis, where both parties benefit, is observed in marine environments between cleaner fishes and their clients. However, the influence of cleaning stations on the movements of large mobile species is not well understood. This study investigated the attendance of reef manta rays at cleaning stations using acoustic telemetry and in-water surveys. The findings showed that manta ray movement and habitat use were associated with the distribution of cleaner wrasse and hard coral substrate. Cleaning interactions took precedence over other behaviours, suggesting manta rays have long-term memory and prefer cleaning sites near productive foraging areas.
Abstract
“1. Mutualism is a form of symbiosis whereby both parties benefit from the relationship. An example is cleaning symbiosis, which has been observed in terrestrial and marine environments. The most recognized form of marine cleaning symbiosis is that of cleaner fishes and their clients.
2. Cleaner species set up cleaning stations on the reef, and other species seek out their services. However, it is not well understood how the presence of cleaning stations influence movements of large highly mobile species. We examined the role of cleaning stations as a driver of movement and habitat use in a mobile client species.
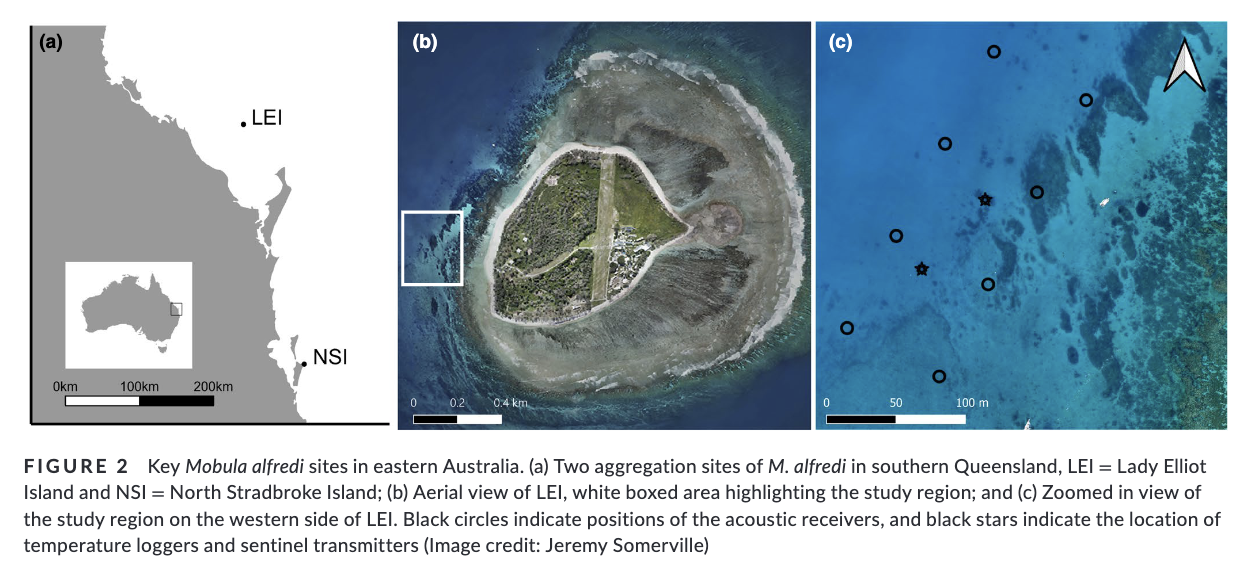
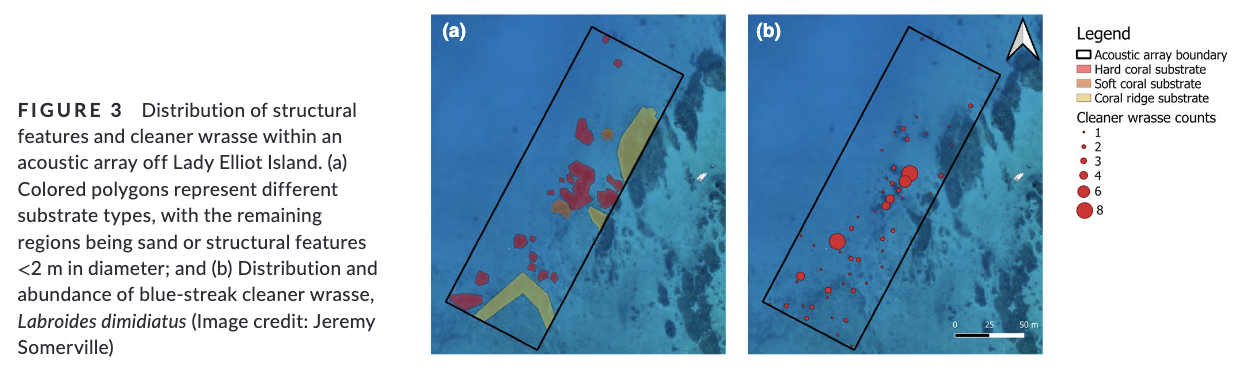
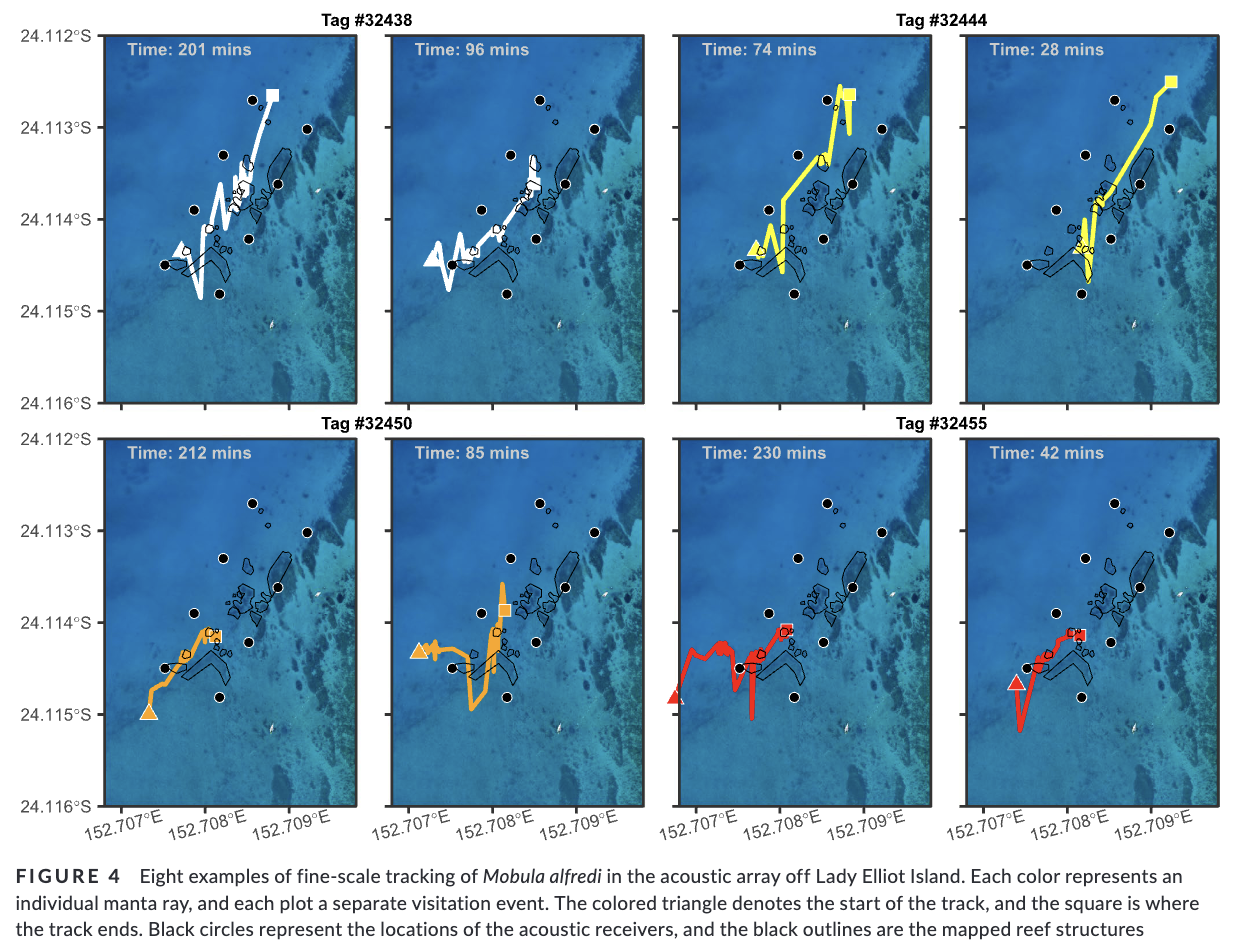
3. Here, we used a combination of passive acoustic telemetry and in-water surveys to investigate cleaning station attendance by the reef manta ray Mobula alfredi. We employed a novel approach in the form of a fine-scale acoustic receiver array set up around a known cleaning area and tagged 42 rays. Within the array, we mapped structural features, surveyed the distribution of cleaner wrasse, and observed the habitat use of the rays.
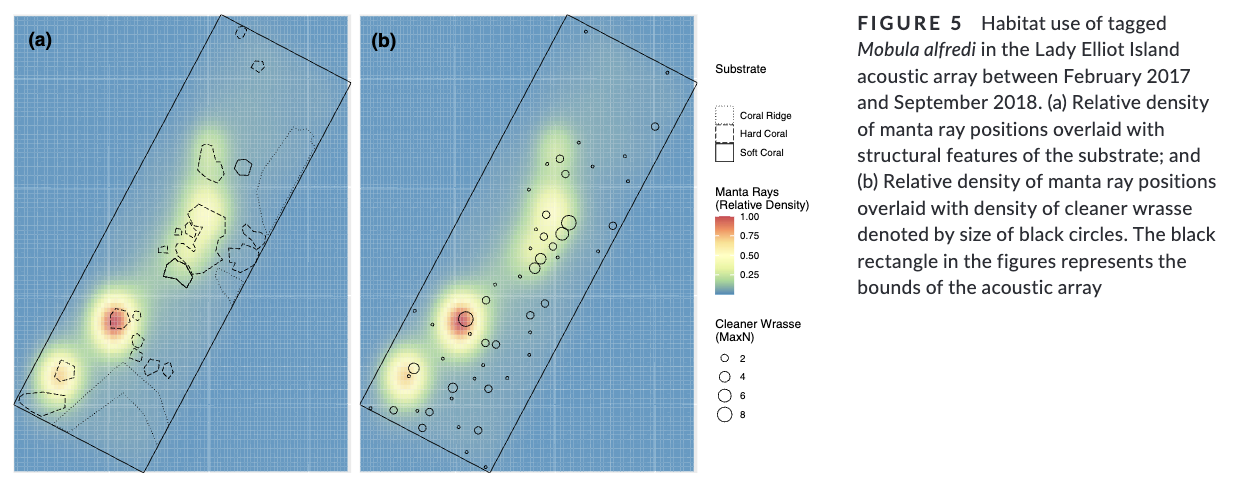
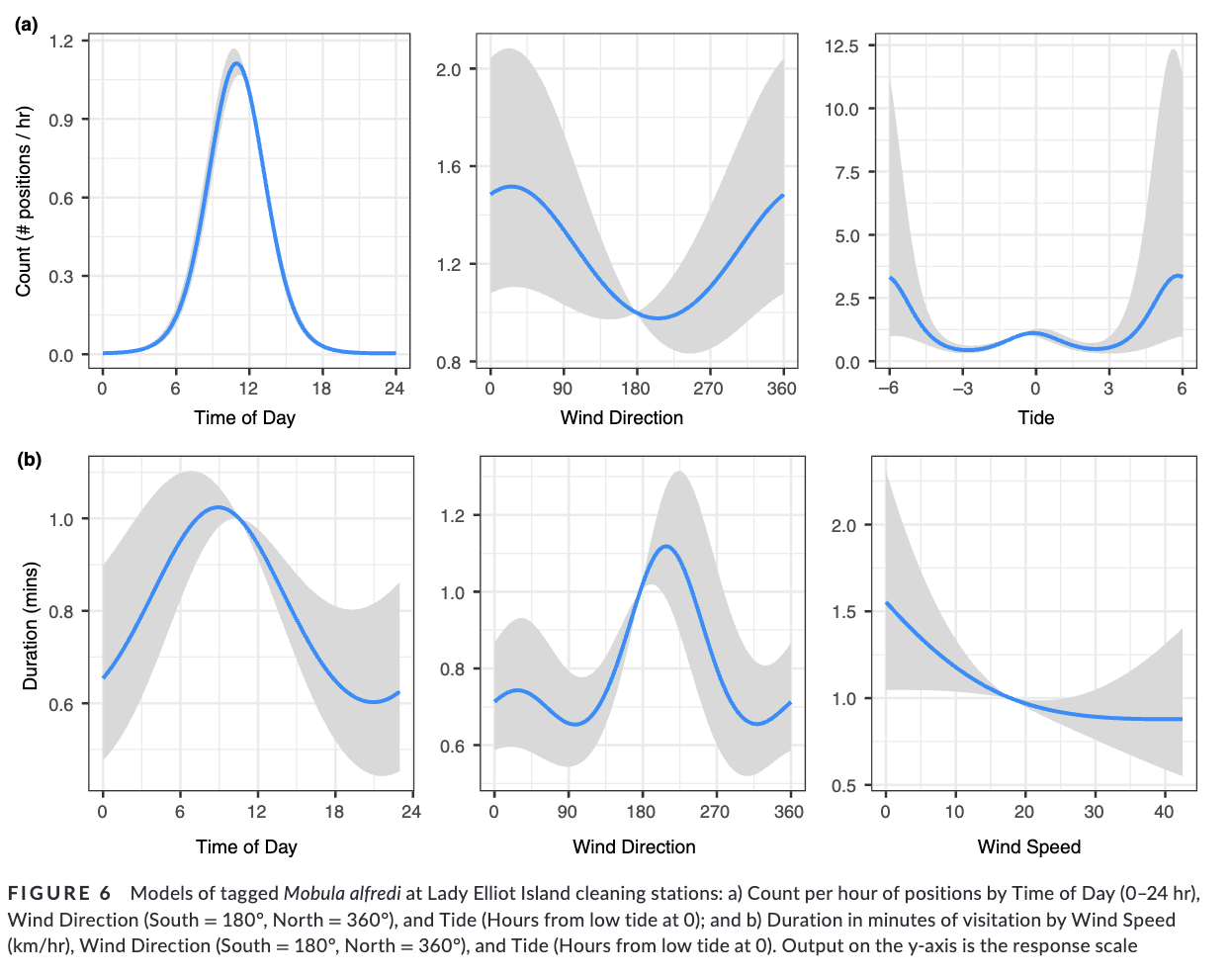
4. We found manta ray space use was significantly associated with blue-streak cleaner wrasse Labroides dimidiatus distribution and hard coral substrate. Cleaning interactions dominated their habitat use at this site, taking precedence over other life history traits such as feeding and courtship.
5. This study has demonstrated that cleaning symbiosis is a driver for highly mobile, and otherwise pelagic, species to visit inshore reef environments. We suggest that targeted and long-term use of specific cleaning stations reflects manta rays having a long-term memory and cognitive map of some shallow reef environments where quality cleaning is provided. We hypothesize that animals prefer cleaning sites in proximity to productive foraging regions.”
Author Affiliation
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland,
Centre for Applications in Natural Resource Mathematics (CARM), School of Mathematics and Physics, The University of Queensland
CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere, Queensland Biosciences Precinct (QBP)
School of Science, Technology and Engineering, University of the Sunshine Coast
School of Biological, Earth, and Environmental Sciences, University of New South Wales
School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Deakin University
Innovasea
Funded by
Australian Research Council
University of Queensland Research Scholarships
Carl F. Bucherer
Save Our Seas Foundation
Four Seasons Resorts Maldives
