Environmental drivers of reef manta ray (Mobula alfredi) visitation patterns to key aggregation habitats in the Maldives
June 2021
Joanna L. Harris & Guy M. W. Stevens
Summary: This study was conducted to understand the habitat use and movement patterns of reef manta rays in three key areas in the Maldives. The study found that reef manta rays exhibit high affinity to the eastern side of Baa Atoll and visitation patterns may be associated with differences in habitat use by sex and maturity status. Wind-driven oceanographic processes, such as Langmuir Circulation, may increase zooplankton concentration and attract manta rays to certain locations. The study suggests that these three areas form part of a network of key habitats that provide essential services to the manta rays, and future conservation efforts should focus on identifying all areas of key habitat use for this species within the Maldives.
Abstract
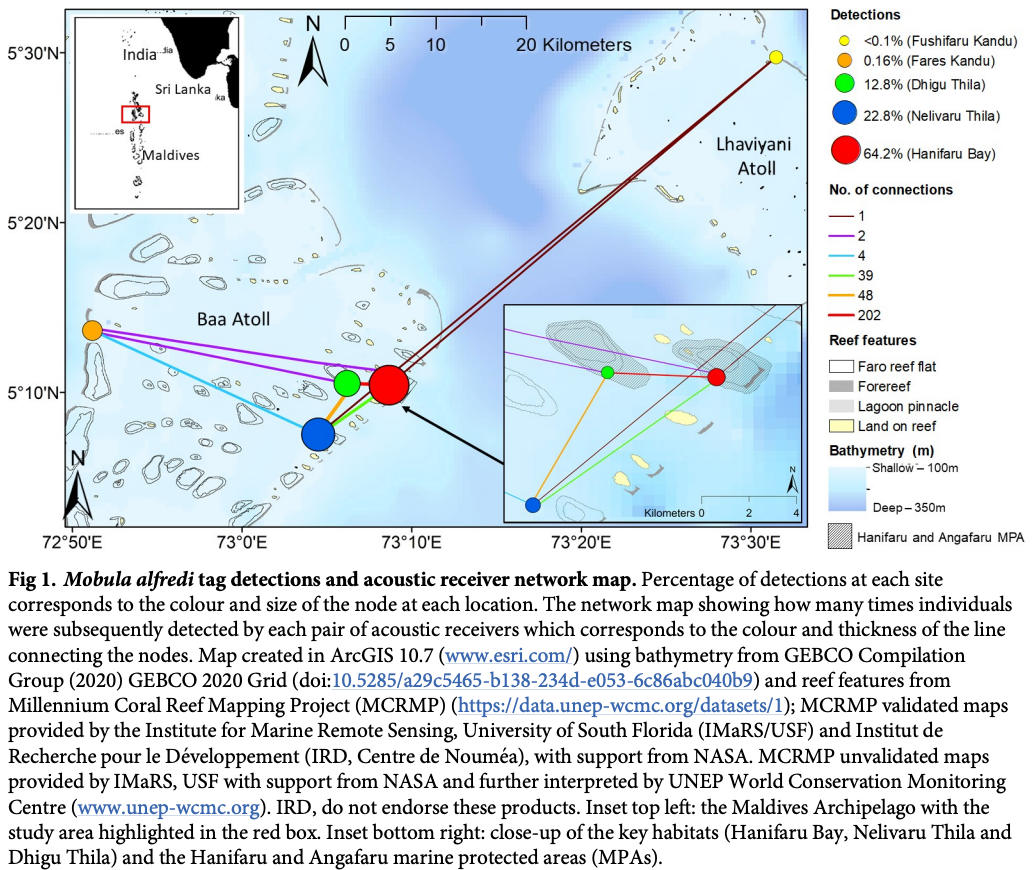
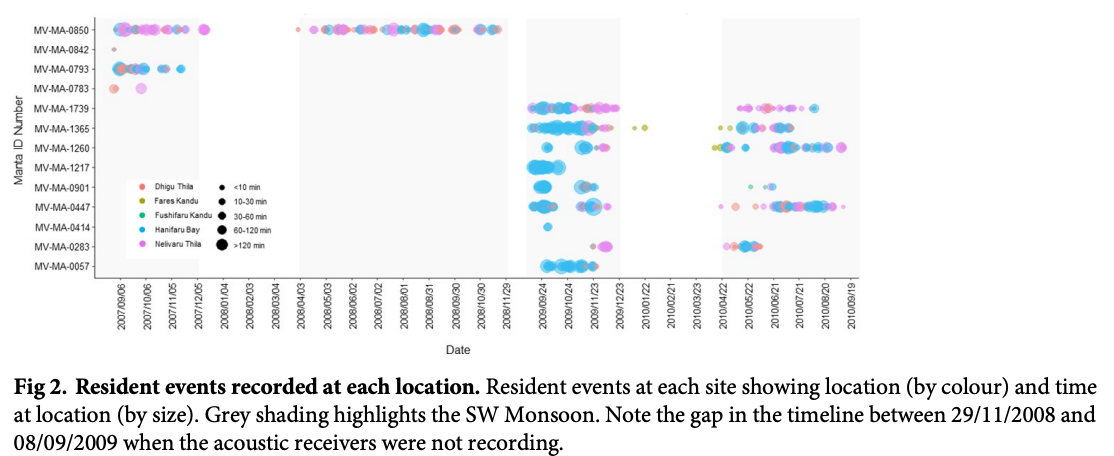
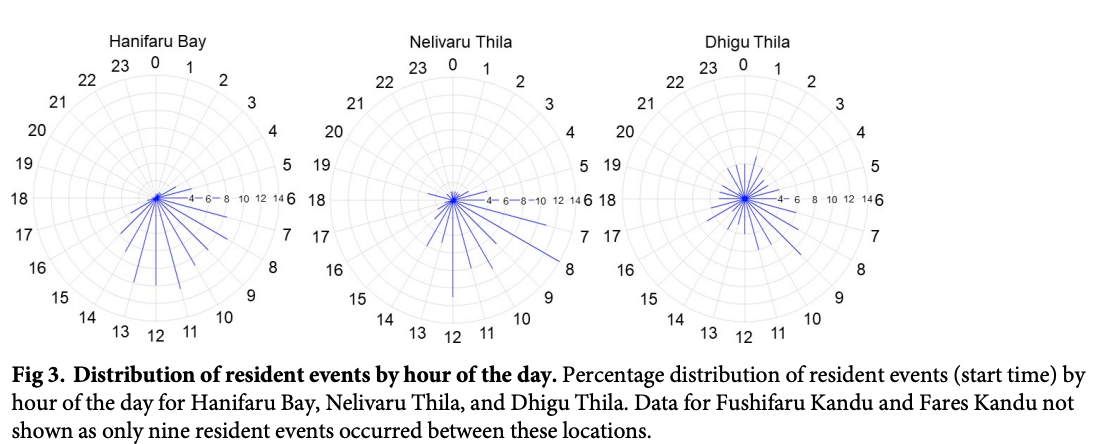
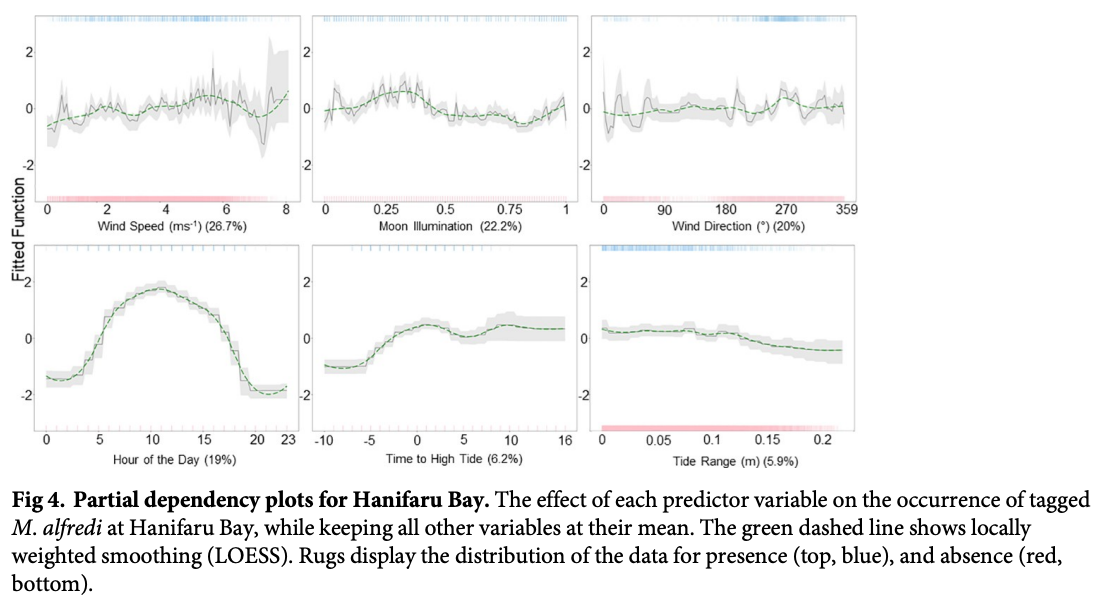
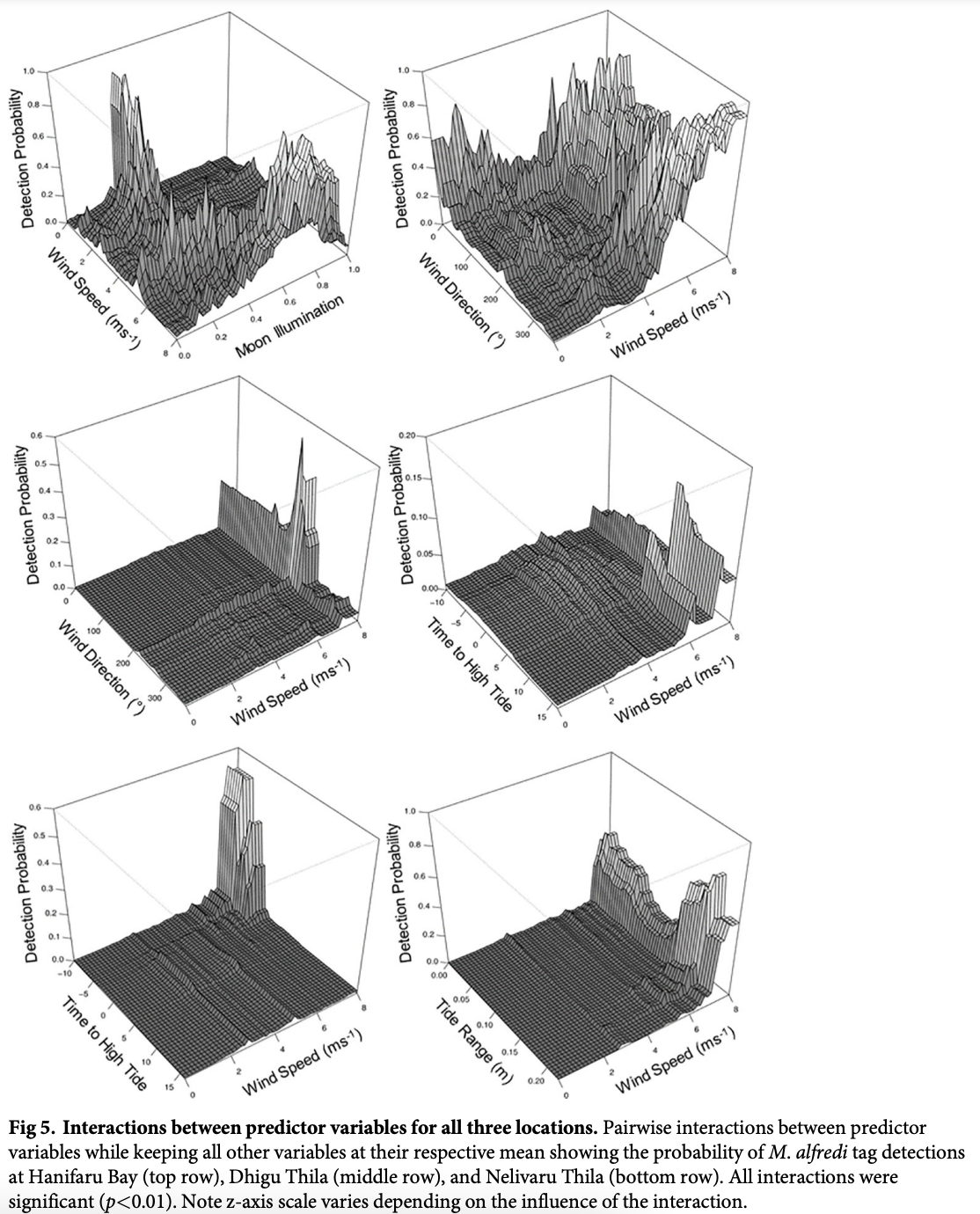
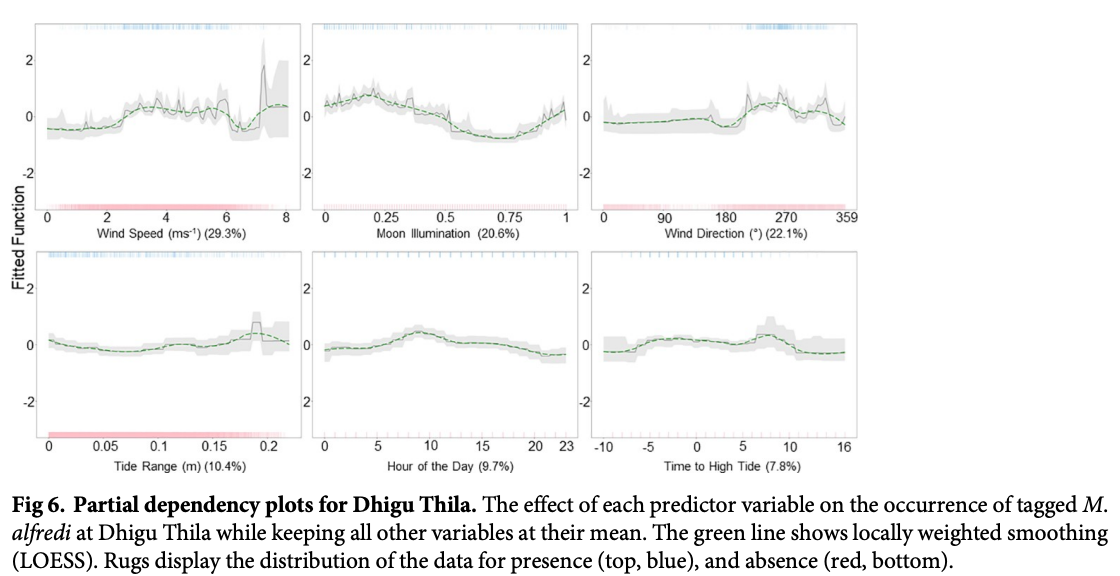
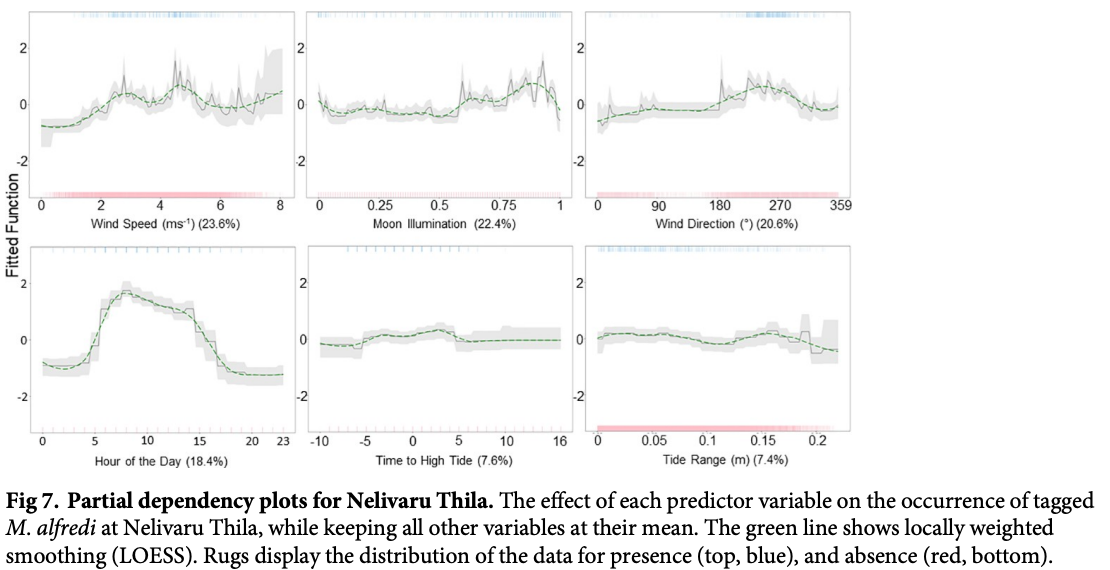
“A detailed understanding of the dynamics of small-scale (10s km) habitat use by the reef manta ray (Mobula alfredi) in the Maldives Archipelago is required to develop an effective national conservation management plan for this wide-ranging species. Here, a combination of photo-ID sightings data and acoustic telemetry were used to investigate both long-term M. alfredi visitation trends and small-scale movement patterns to key habitats on the eastern side of Baa Atoll (Hanifaru Bay feeding area, Dhigu Thila multifunctional site, and Nelivaru Thila cleaning station). All tagged and most of the sighted M. alfredi exhibited high affinity to the eastern side of Baa Atoll, where 99% of detections occurred, and 69% of individuals were re-sighted in multiple years. Sightings data suggests that visitation patterns may be associated with differences in habitat use by sex and maturity status. Boosted regression trees indicated that tag detection probability at Hanifaru Bay increased with increased westerly wind speed (>5ms-1) during the day, close to a new and full moon just after high tide, and when the tidal range was low. Interaction effects between predictors suggest that wind-driven oceanographic processes, such as Langmuir Circulation, maybe working to increase zooplankton concentration at this location. Tag detection probability increased at Dhigu Thila under similar conditions. At Nelivaru Thila, it increased at lower wind speeds (<5ms-1), close to a full moon, three hours after high tide. These results suggest that M. alfredi may utilise cleaning stations during the day when environmental conditions are not suitable for feeding. There was a high level of connectivity between these three locations, which suggests they form part of a network of key habitats that provide essential services to M. alfredi locally. Future conservation efforts should focus on identifying all areas of key habitat use for this species within the Maldives; applying strict protective measures to these sites and any connecting migration corridors which link them.”
Infographics
Author Affiliations
The Manta Trust
University of Plymouth
Funded by
Save Our Seas Foundation



